The Future of Autonomous Vehicles: Advancements, Challenges, and Implications
by Sovina Vijaykumar

AVs will revolutionize transportation soon. Technology has made it possible to develop vehicles that operate without human intervention. These autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce accidents, increase efficiency, and enhance the overall transportation experience. This blog covers the latest advances in autonomous vehicle technology, the regulatory and ethical challenges, and the potential implications for transportation’s future.
Latest Advances in Autonomous Vehicle Technology:
The latest advances in autonomous vehicle technology have been made possible by the development of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies have enabled the creation of vehicles that can sense their surroundings, interpret data, and make decisions in real time.
One of the most significant breakthroughs in AV technology is the development of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors. LiDAR sensors use laser beams to create a 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings, allowing it to navigate through complex environments such as crowded cities and highways. LiDAR sensors can detect and track other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles in real-time.
AV technology has also advanced through the use of deep learning algorithms. The algorithms enable the vehicle to learn from past experiences and make data-driven decisions. For example, if an autonomous vehicle encounters a particular road condition or driving situation, it can learn from that experience and apply that knowledge to similar situations in the future.
Companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Cruise are at the forefront of AV technology development. Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google), developed a fully autonomous vehicle fleet that has driven over 20 million miles on public roads. Tesla’s Autopilot system, currently used in over 1 million Tesla vehicles worldwide, has also made significant strides in AV technology. Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors, has developed a self-driving car that does not have a steering wheel or pedals.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges:
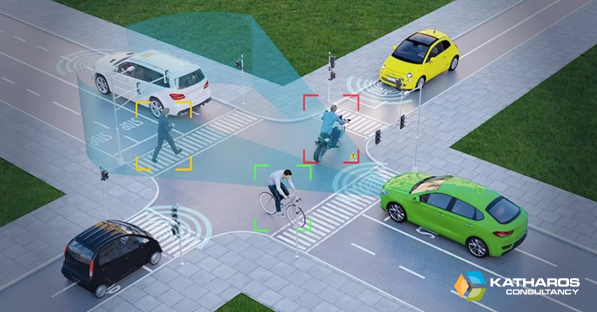
Before autonomous vehicles can become a reality, we must address several regulatory and ethical challenges that create obstacles to their widespread adoption. One of the primary concerns is safety. Designers must ensure that AVs can safely operate in all driving conditions, including adverse weather, complex traffic situations, and unexpected obstacles.
Another challenge is a liability. In the event of an accident involving an AV, who is responsible? Is it the manufacturer, the software developer, or the vehicle operator? We must determine the answer to this question before widely adopting AVs.
Privacy is also a significant concern. AVs collect vast amounts of data about their surroundings, passengers, and operators. This data must be collected, stored, and used responsibly to protect the privacy of individuals.
Finally, there are ethical concerns surrounding AVs. For example, if an autonomous vehicle must choose between saving the lives of its occupants or those of pedestrians, what decision should it make? We must address these ethical questions to ensure that AVs align with society’s values when operating.

Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., is one of the most advanced companies in AV technology development. Waymo’s autonomous vehicles have driven more than 20 million miles on public roads, making it one of the most experienced AV companies in the world. Waymo addresses the regulatory and ethical challenges of AV adoption in several ways.
Safety: Waymo has designed its vehicles to operate safely in all driving conditions. Waymo’s vehicles use LiDAR sensors to create a 3D map of their surroundings, which enables them to detect and avoid obstacles in real time. Cameras, radar sensors, and other technologies equip vehicles to navigate complex traffic situations.
Liability: Waymo partnered with insurance companies to develop insurance coverage for AVs. This coverage will include the vehicle and powering software to determine liability in the event of an accident.
Privacy: Waymo is committed to protecting the privacy of its passengers and has developed strict data privacy policies to ensure that the data collected by its vehicles is collected, stored, and used responsibly.
Ethical Concerns: To address ethical concerns surrounding AVs, Waymo has taken a transparent approach. In 2019, Waymo published a blog post outlining how it handles complex decisions. According to the post, Waymo programs its vehicles to prioritize the safety of all individuals, including pedestrians, cyclists, and other drivers. The AVs also avoid situations where a discernible safe route isn’t evident.
Tesla, founded by Elon Musk, is another company at the forefront of autonomous vehicle technology. Tesla’s Autopilot system has been a game-changer in the AV industry. The system uses a combination of cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to detect and respond to road conditions. The system can automatically steer, accelerate, and brake the vehicle, making it semi-autonomous.

Tesla has faced criticism and scrutiny over the safety of its Autopilot system. In May 2016, a Tesla Model S crashed while on Autopilot, killing the driver. The incident raised questions about the responsibility of autonomous vehicle manufacturers. Tesla responded by adding safety features and improving Autopilot’s capabilities.
Tesla has also faced regulatory challenges. In 2018, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) released a report that identified Tesla’s Autopilot system as a contributing factor in a fatal crash involving a Tesla Model X. The NTSB recommended that Tesla improve Autopilot’s ability to detect and respond to other vehicles on the road.

Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors, is another company working on developing autonomous vehicles. Cruise’s self-driving car, the Cruise Origin, does not have a steering wheel or pedals. The ride-sharing service is for passengers.
Cruise collaborates with regulatory agencies to address safety and ethical concerns for AVs. California granted Cruise the first permit to test AVs without a safety driver in 2018. The company also works with federal agencies to establish safety standards for AVs.
In 2020, Cruise released a safety report outlining the safety features and protocols in place for its autonomous vehicles. The report detailed the vehicle’s safety systems, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, and the safety protocols that the company has in place to monitor and maintain them.
Implications for the Future of Transportation:
Autonomous vehicles could drastically impact the transportation industry. They may lessen traffic, increase safety, and enhance accessibility for non-drivers, such as older adults or individuals with disabilities.
One potential use for AVs is in ride-sharing services. Using autonomous vehicles in ride-sharing services could cut the number of cars on the road, thereby reducing traffic congestion and emissions.
Another potential use for AVs is in the shipping and logistics industry. AVs could transport goods, reducing the need for human drivers and improving efficiency.
AVs could impact urban planning. Fewer parking spaces would free up valuable real estate in cities. AVs could drop off passengers and self-park outside the city center, lessening the need for parking garages and lots.
However, the widespread adoption of AVs could also have negative implications. The use of AVs could lead to job loss in the transportation industry. The shift towards AVs could worsen existing inequalities, as those who cannot afford AVs may have limited transportation options.
Another potential issue is the impact on energy consumption and the environment. AVs could reduce emissions by optimizing routes and reducing congestion. However, their use of advanced technologies may also raise energy consumption.
We must address regulatory and ethical challenges to maximize the benefits of AVs while reducing their negative implications. Establishing safety standards, liability frameworks, and data privacy policies will be vital to ensure their ethical and safe operation.
Conclusion:
AVs will revolutionize the way we travel, and their rise is inevitable. Rapid advancements in technology enable AVs to operate without human intervention. Waymo, Tesla, and Cruise are leaders in AV technology development, addressing regulatory and ethical challenges for AV adoption.

The potential implications of AVs on the transportation industry are vast, including reduced traffic congestion, improved safety, and increased accessibility. However, there are also potential negative implications, including job loss and increased energy consumption.
We must address regulatory and ethical challenges to ensure AVs operate safely and ethically. Safety standards, liability frameworks, and data privacy policy development will be crucial to align AV adoption with society’s values.
Overall, the future of autonomous vehicles is exciting, and continued advancements in technology and a commitment to addressing regulatory and ethical concerns will be critical in realizing the full potential of AVs.